[ad_1]
By Kai Novak – Tech Innovation Specialist
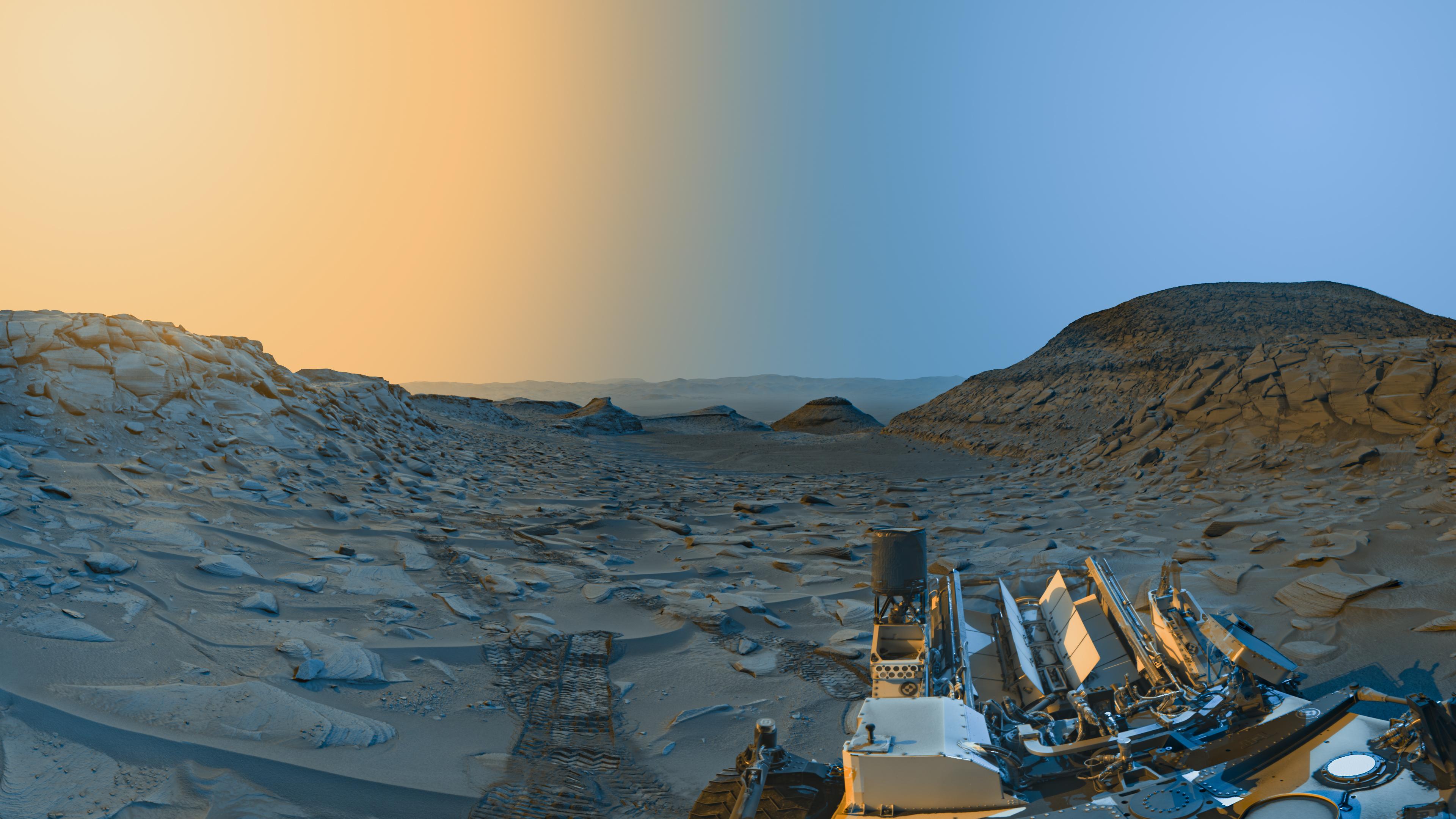
Imagine standing on the rugged slopes of an alien mountain, gazing across a vast crater floor etched by ancient rivers, with the distant rim fading into a hazy horizon under shifting Martian light. That’s the breathtaking vista NASA’s Curiosity rover gifted us at the tail end of 2025, a composite panorama that blends dawn’s cool blues with afternoon’s warm yellows for a serene portrait of the Red Planet unlike any before. As I debugged my latest AI app under the glow of my smart desk lamp last weekend, this image popped up in my feed, reminding me how space tech continues to bridge worlds—literally. This serene Mars image from a NASA rover isn’t just eye candy; it’s a testament to human ingenuity, revealing clues about a planet that might have once harbored life. In this deep dive, we’ll unpack the magic behind the shot, the rover’s tech wizardry, and what it means for our cosmic future, all while spotlighting innovations that bring space exploration closer to home.
What Makes This Serene Mars Image So Special?
This isn’t your average snapshot—it’s a meticulously crafted composite that captures the ethereal beauty of Mars in a way that feels almost poetic. Taken from the lower foothills of Mount Sharp inside Gale Crater, the image merges two black-and-white panoramas: one from the crisp Martian morning and another from the early evening. NASA engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory added color post-capture, using blue tones for the dawn view and yellow for the afternoon, to highlight subtle landscape details that might otherwise go unnoticed.
The result? A vista that showcases the rover’s wheel tracks snaking back to Valle de la Luna, a recent drilling site, while the crater’s rim looms 25 miles away. Boxwork formations—rugged ridges formed billions of years ago by mineral-hardened cracks eroded by wind—dominate the foreground, painting a picture of Mars’ dynamic geological history. As someone who’s tinkered with image-processing algorithms in my urban loft, I appreciate how this technique mimics advanced AI enhancement tools, turning raw data into something profoundly inspiring.
Caption: NASA’s Curiosity rover’s composite panorama of Gale Crater, blending morning blue and afternoon yellow light for a serene Martian view.
Alt text: Serene Mars image from NASA rover showing Gale Crater in composite colors.
Behind the Scenes: How Curiosity Captured This Stunning Panorama
Curiosity didn’t just point and shoot—this serene Mars image from a NASA rover required precise orchestration. The rover’s Mastcam and Navcam instruments snapped the originals toward the end of 2025, specifically around Sols 4722 and 4723 (Martian days). Positioned on a boxwork ridge, Curiosity used its robotic arm and cameras to document the scene, transmitting data back to Earth for processing.
The process highlights the rover’s resilience: Launched in 2011 and landing in Gale Crater in 2012, Curiosity was built for a two-year mission but has clocked over 4,000 sols thanks to nuclear-powered reliability and software updates. Its suite of 17 cameras, including high-res color Mastcams, captures everything from wide-angle landscapes to microscopic rock textures, aiding scientists in piecing together Mars’ watery past.
For tech enthusiasts like me, who geek out over remote operations during weekend coding sessions, this echoes modern IoT devices—think smart home cams beaming live feeds. Dive deeper into similar innovations with our guide on understanding AI assistants today.
The Cutting-Edge Tech Powering NASA’s Mars Rovers
At the heart of this serene Mars image from a NASA rover lies groundbreaking technology that’s evolved space exploration. Curiosity’s plutonium-238 radioisotope thermoelectric generator provides steady power, while its ChemCam laser zaps rocks to analyze composition from afar—a real-life sci-fi tool.
Navigation relies on AI-driven hazard avoidance, similar to self-driving cars here on Earth. The rover’s wheels, redesigned after early wear, traverse treacherous terrain, and its drill collects samples sealed for future return missions. This tech synergy has allowed Curiosity to climb Mount Sharp, a 3-mile-tall peak layered with sedimentary records of ancient lakes and rivers.
Drawing parallels to my AI side projects, these systems foreshadow advancements in autonomous robotics. For a broader look, check out exploring AI tools for jobs, where similar algorithms boost efficiency.
Caption: Close-up view of NASA’s Curiosity rover on Mars, showcasing its advanced cameras and robotic arm used for capturing panoramas.
Alt text: NASA Curiosity rover technology in action on Mars surface for serene image capture.
What This Image Reveals About Mars’ Ancient Past
Beyond its beauty, this serene Mars image from a NASA rover unlocks secrets of the planet’s history. Gale Crater, a 96-mile-wide impact basin, once held a lake system, as evidenced by the layered sediments on Mount Sharp. The boxwork ridges suggest water percolated through cracks, depositing minerals that hardened over eons—clues to a wetter, potentially habitable Mars 3.5 billion years ago.
Scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory note that wind erosion sculpted these features, exposing ridges that tell tales of environmental shifts. Recent samples from nearby sites like Nevado Sajama could reveal organic compounds, bolstering theories of past microbial life.
As I reflect on this during my coffee-fueled coding marathons, it underscores how tech reveals our universe’s mysteries. Link this to earthly innovations in thea energy unveils pixel-inspired fusion plant, pushing energy boundaries.
The Scientific Insights from Gale Crater’s Boxwork Formations
Zooming in on the boxwork in this serene Mars image from a NASA rover, these vein-like structures formed when groundwater minerals filled rock fractures, later exposed by erosion. This process mirrors Earth’s geological features, offering comparative planetology insights.
Curiosity’s instruments, like the Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons, detect hydrogen (a water proxy), confirming hydrated minerals. Such data informs models of Mars’ climate evolution from wet to arid, crucial for future human missions.
For gadget lovers, this echoes sensor tech in wearables—track your own explorations with the exact Oura Ring I use for sleep and activity metrics.
Caption: Detailed boxwork formations in Gale Crater captured by Curiosity, highlighting ancient mineral veins.
Alt text: Boxwork ridges on Mars in serene NASA rover image revealing geological history.
How Lighting Changes Transform Mars’ Landscape in Photos
The dual-time capture in this serene Mars image from a NASA rover illustrates how Martian light shifts dramatically. Morning shots reveal cooler shadows, emphasizing textures, while afternoon light warms the scene, highlighting dust hues.
This technique, akin to HDR photography, enhances scientific analysis by revealing atmospheric dust effects. Mars’ thin atmosphere scatters blue light during sunsets, opposite to Earth’s—hence the stylized colors.
Tie this to photography gadgets: Enhance your shots with a portable solar charger for off-grid adventures.
Future Missions: What’s Next for NASA’s Rovers on Mars
Building on this serene Mars image from a NASA rover, NASA’s Perseverance rover in Jezero Crater collects samples for the Mars Sample Return mission, set for the 2030s. Future concepts like Dragonfly to Titan expand rotorcraft tech.
These advancements promise more vivid imagery and data, potentially confirming past life. As a software engineer, I’m excited for AI’s role in autonomous navigation.
Explore more on apple drops new airpods pro firmware update, showcasing wireless tech parallels.
Caption: NASA’s Perseverance rover, successor to Curiosity, exploring Jezero Crater for future Mars insights.
Alt text: Perseverance rover on Mars, advancing tech beyond serene Curiosity image.
Inspiring the Next Generation of Space Innovators
This serene Mars image from a NASA rover ignites curiosity in young minds, much like my early fascination with coding sparked by sci-fi. Programs like NASA’s Artemis aim to land humans on Mars by the 2040s, blending robotics with crewed exploration.
Encourage STEM pursuits with tools like a meditation headband for focus during study sessions.
Essentials List: 7 Must-Have Amazon Products to Fuel Your Space Enthusiasm
To dive deeper into space tech from home, here are seven essentials—currently 30% off on some, so run:
- Oura Ring – Tracks health metrics like NASA astronauts.
- Portable Solar Charger – Powers gadgets off-grid, mimicking rover energy.
- Red Light Therapy Lamp – Boosts recovery, inspired by space health tech.
- Essential Oils Diffuser – Creates a serene atmosphere for stargazing.
- Sunrise Alarm Clock – Simulates Martian dawn for better sleep.
- Blue Light Glasses – Protects eyes during late-night rover image browsing.
- Insulated Bottle – Keeps drinks hot or cold for exploration outings.
Must-Read Books for Space Exploration Enthusiasts
Expand your horizons with these five captivating reads:
- “The Martian” by Andy Weir – Survival ingenuity on the Red Planet.
- “Packing for Mars” by Mary Roach – Humorous take on space life.
- “Endurance: A Year in Space” by Scott Kelly – Real astronaut experiences.
- “Hidden Figures” by Margot Lee Shetterly – Unsung heroes of NASA.
- “Pale Blue Dot” by Carl Sagan – Philosophical view of our place in the cosmos.
Link to Amazon: “The Mindful Body” book – For mindful tech integration.
Common Mistakes in Interpreting Mars Images and How to Avoid Them
Don’t assume colors are real—many are enhanced for science. Cross-reference with NASA’s raw images for authenticity.
Tips for Viewing and Sharing NASA Rover Images
Download from official sites like NASA’s image gallery and use apps for virtual Mars tours.
Caption: Spectacular Martian landscape from Curiosity, emphasizing the serene beauty of Gale Crater.
Alt text: Breathtaking Mars panorama in serene NASA rover image.
This serene Mars image from a NASA rover reminds us that technology unlocks wonders beyond our world. As we push boundaries, innovations like these inspire everyday breakthroughs.
FAQ
What rover captured this serene Mars image? NASA’s Curiosity rover took the shots in Gale Crater, combining them into a composite.
When was this Mars panorama captured? Toward the end of 2025, around Sols 4722-4723.
Why does the image have blue and yellow colors? Colors were added post-capture to represent morning (blue) and afternoon (yellow) light, enhancing details.
What does this image reveal about Mars? It shows ancient water-formed boxwork ridges, hinting at a habitable past.
How can I see more NASA rover images? Visit NASA’s raw image archives for Curiosity and Perseverance.
What’s next for Mars exploration? Sample return missions and human landings in the 2030s.
P.S. Ready to geek out on more tech marvels? Sign up for my free tech innovation guide and get monthly updates straight to your inbox!
Related Posts
- Thea Energy Unveils Pixel-Inspired Fusion Plant
- Apple Drops New AirPods Pro Firmware Update
- Whatsapp Is Rolling Out New Features to Jazz Up Your New Years Greetings
- Ayaneos Latest Game Boy Remake Will Have an Early Bird Starting Price of 269
- How to Simplify Complex Excel Formulas for Better Auditing
- 18 Best Gifts for Always Cold People in 2025
[ad_2]